Shrimp
How Early Detection Helps Shrimp Farmers Avoid Losses
Highlight

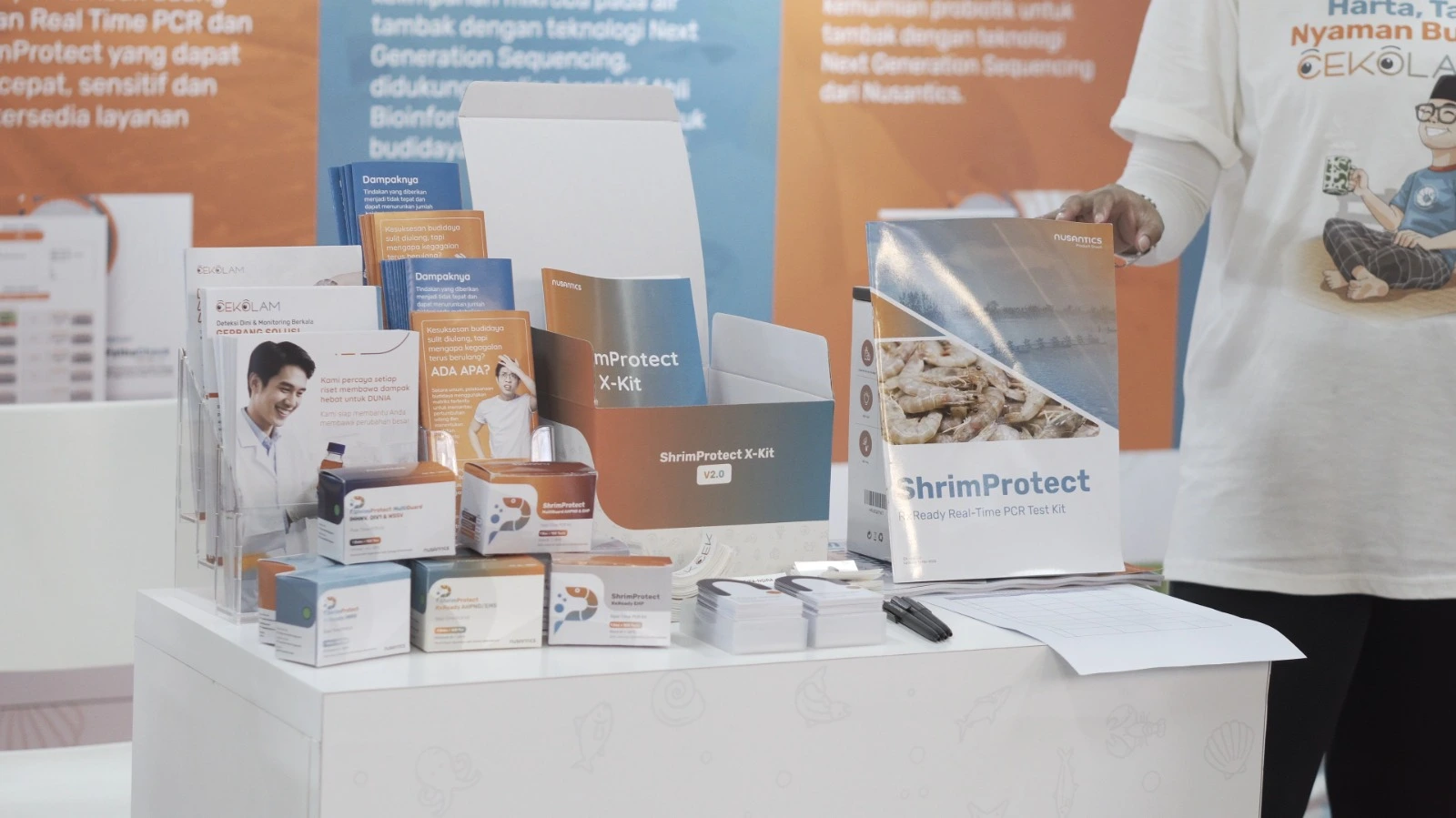
ShrimProtect AHPND/EMS
Highlight

ShrimProtect AHPND/EMS

February 12, 2024
Nusantics Luncurkan PathoScan hrHPV qPCR Kit untuk Skrining/Pemeriksaan HPV dengan Menggunakan Urine dan Swab Serviks

July 20, 2023
CeKolam by Nusantics: A Modern Solution to Boost Shrimp Production in Indonesia
Knowledge Hub
Menu
Find Us
Mon - Fri: 9 a.m. - 6 p.m.
i3L Campus @ Lvl. 3
Jl. Pulomas Barat No.Kav.88, RT.4/RW.9, Kayu Putih, Pulo Gadung,
Jakarta Timur 13210
Contact Us
hello@nusantics.com
+62 (21) 509 194 30
Copyright © 2026 PT Riset Nusantara Genetika, PT Nusantara Butuh Diagnostik. All Rights Reserved.Privacy Policy
© 2026 PT Riset Nusantara Genetika.
Privacy Policy